Castello di Carsoli
- View a machine-translated version of the Italian article.
- Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia.
- Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article.
- You must provide copyright attribution in the edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an interlanguage link to the source of your translation. A model attribution edit summary is
Content in this edit is translated from the existing Italian Wikipedia article at [[:it:Castello di Carsoli]]; see its history for attribution. - You may also add the template
{{Translated|it|Castello di Carsoli}}to the talk page. - For more guidance, see Wikipedia:Translation.

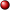
Castello di Carsoli (Italian for Castle of Carsoli) is a medieval castle in Carsoli, Province of L'Aquila (Abruzzo), central Italy.[1][2][3]
History
The medieval village of Carsoli was built as a cluster of houses around the church of Santa Maria in Cellis not far from the remains of the Roman colony of Carseoli (or town of Carsioli), dating from the early fourth century BC, located in the neighboring town of Civita di Oricola. The village was destroyed by the Saracens in the tenth century, and between 996 and 1000, Count Rinaldo of the Marsi accounts initially built on Sant'Angelo hill a lookout tower, which was then subject to expansions with the construction of walls according to the castle-yard layout, the latest being the renovation of Anjou in 1293.
The territory of Carsoli and the Santa Maria church in Cellis were donated by Count Rainaldo the monastery of Subiaco. Later the castle was owned by Albe accounts, then of Tagliacozzo barons, then by the Orsini and Colonna until 1806, the subversion of feudalism
Architecture
The plan of the castle is in the shape of a "L", with strong walls. The interior has been lost due to bad storage conditions in past centuries. A large watch tower survives.
References
- ^ Latini, Marialuce (2000). "Carsoli (AQ), Il castello-recinto". Guida ai Castelli d'Abruzzo (in Italian). Pescara: Carsa Edizioni. p. 96. ISBN 88-85854-87-7.
- ^ Luciano Di Gregorio (20 February 2013). Bradt Abruzzo. Bradt Travel Guides. p. 165. ISBN 978-1-84162-446-4.
- ^ Dana Facaros; Michael Pauls (2003). Central Italy. New Holland Publishers. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-86011-112-9.
External links

- "Castello di Carsoli" (in Italian). Regione Abruzzo. Archived from the original on 10 April 2016. Retrieved 8 May 2016.
- "Carsoli" (in Italian). Archeoclub L'Aquila. Archived from the original on 13 February 2020. Retrieved 8 May 2016.
42°06′05″N 13°05′16″E / 42.1013°N 13.0878°E / 42.1013; 13.0878
- v
- t
- e











